In addition to relational databases, those that follow a non-relational structure - also known as NoSQL databases - can also be used for the structured storage of data. A subcategory of these are so-called document-oriented databases, in which, as the name suggests, data is stored in the form of documents. This is particularly advantageous when a flexible data structure is required and complex, unstructured data needs to be browsed in the shortest possible time.
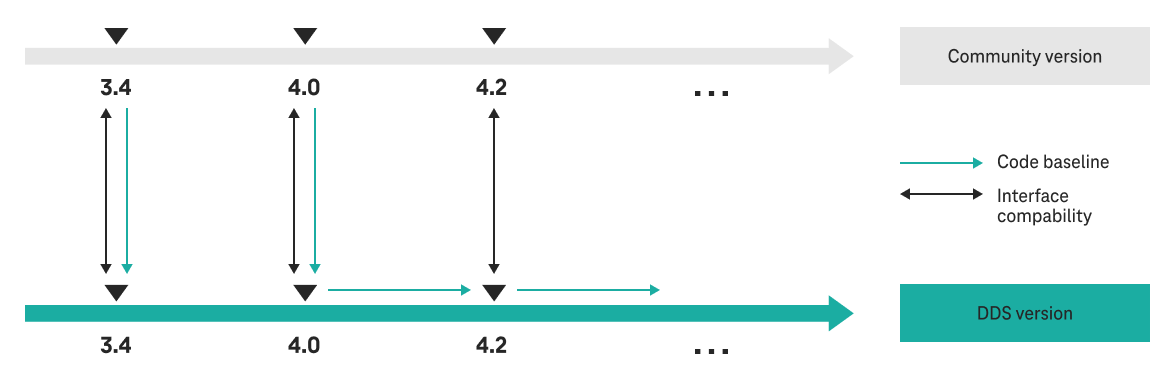
The Open Telekom Cloud also offers a document-oriented database: Our corresponding service is called Document Database Service (DDS). DDS is a cloud database service. This is particularly suitable for database applications that require simple scalability, maximum availability and flexible adaptability.