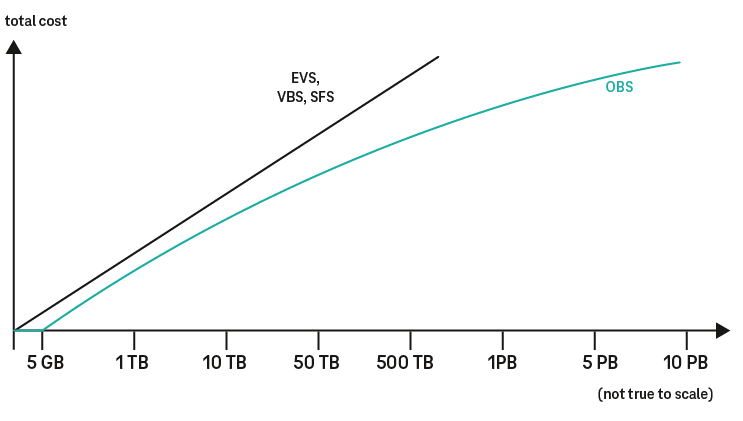
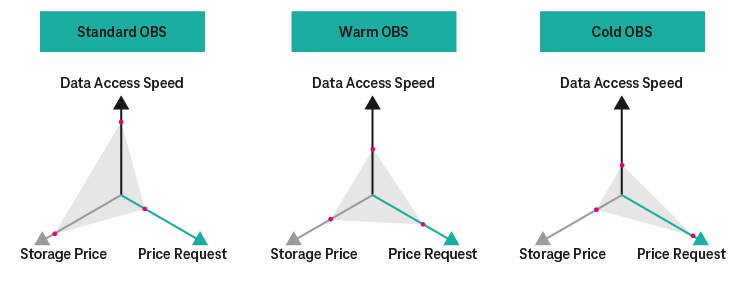
The Open Telekom Cloud offers five storage types: Elastic Volume Service (EVS, block storage – always linked to virtual machines), Object Storage Service (OBS), Cloud Server/Volume Backup Service (CSBS/VBS), Storage Disaster Recovery Services (SDRS), and Scalable File Storage (SFS). The pricing models vary between the object storage and the block-storage offers (EVS, VBS). In general, object storage is VM-independent and a more cost-effective storage option, whereas block storage enables fast data access thanks to a directly connected virtual hard drive.
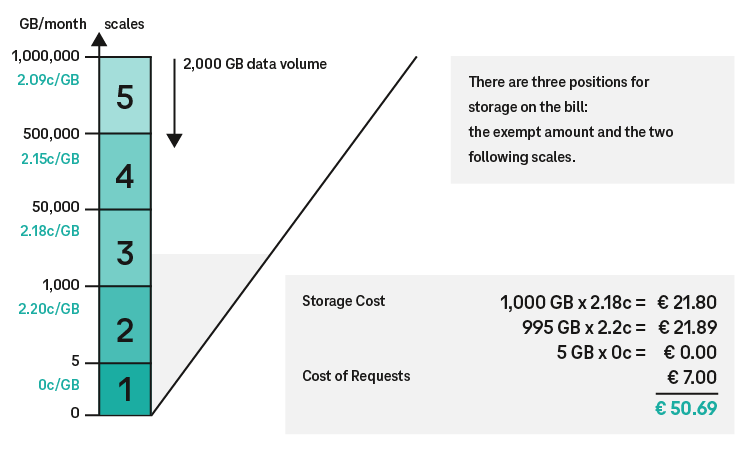
The reference period here is also the relevant calendar month. The average volume of allocated storage is determined (in GB, 1 GB = 1,073,741,824 Byte) and used as the basis for billing. In the block storage option, prices rise on a linear basis in line with the data volume. For object storage, prices are based on (discounted) stepped scales. The scales are of specific sizes and stack on top of each other. The higher the scale, the lower the costs for the storage volumes allocated in that scale. The exception to this rule is that the basic volume of 5 GB for standard object storage is free of charge.
The Storage Disaster Recovery Service (SDRS) is billed in the same way as the EVS. The service features the mirroring of hard disks across two availability zones (AZ). An additional hard disk for data replication in the target AZ is deployed. The additional and the original EVS are billed, as well as a service fee. The fee depends on size of the disks and whether the disks are shared or not. Usually, creating the necessary ECS copy in the second data center does not result in any further computing costs. The ECS only becomes active in the event of a disaster recovery and then generates the regular ECS costs.
Cold object storage is billed in the same way as for standard object storage. Cold object storage uses a low-cost, “slow” storage medium and stores data in compressed form. It is suitable for data that is to be called up and recovered on rare occasions only. The data storage is very cost-effective, but recovery results in additional costs. Recovery takes place on standard object storage as a cache. This is not included in the free contingent and is added to the monthly bill. The recovery process also incurs costs depending on the speed. Data can be called up at three speeds: bulk, standard, and expedited. The bulk request is the slowest but also the most cost-effective, while expedited recovery is the most expensive option. Expedited restoration is prioritized/preferred over other restorations. Since the object storage is designed for the long-term storage of data, there is a minimum storage period of 90 days. If this period is not achieved due to the early deletion of data, the difference to the minimum storage period is calculated and billed according to the rate of the first scale.
Warm object storage behaves similarly to standard object storage in terms of data transfer and requests, but has more favorable storage costs and slightly higher costs for requests. Similar to standard object storage, data is not retrieved as quickly either. Therefore warm object storage is particularly suited to medium-term data storage with a minimum storage period of 30 days. If this period is not achieved due to the early deletion of data, the difference to the minimum storage period is calculated and billed with according to the rate of the first scale.