GeminiDB is a fully managed, cloud-native, distributed NoSQL database service that is fully compatible with open-source Apache Cassandra™ version 3.11 and 4.0. GeminiDB is designed for high availability, scalability, and operational simplicity, where GeminiDB separates compute and storage layers to enable flexible, rapid scaling of resources – compute can be scaled within minutes, and storage within seconds – meeting the demands of dynamic, business-critical workloads.
Offering seamless integration with the robust Open Telekom Cloud ecosystem, GeminiDB features one-click deployment, automated and customizable backup and restore (supporting up to 732-day retention), fine-grained monitoring and alerting, secure data isolation, and enterprise-grade backups to OBS (Object Storage Service). The service supports automated maintenance tasks, visualized resource and performance management, rich tagging and policy controls, and advanced auditing for compliance.


A multi-layer security system, including VPC, subnet, security group, SSL, and fine-grained permission control ensures database security and user privacy.
You can deploy an instance across three Availability Zones (AZs) and quickly back up or restore data to improve data reliability.
The distributed architecture provides superlative fault tolerance (N-1 reliability).

GeminiDB gives you 3 times the performance of the open-source version. Data can be written to this high availability database 24/7, and with automated load balancing and elastic scaling you always have all the performance you need.
Decoupled compute and storage allow you to add compute nodes in minutes and scale up storage capacity in seconds without service interruptions.
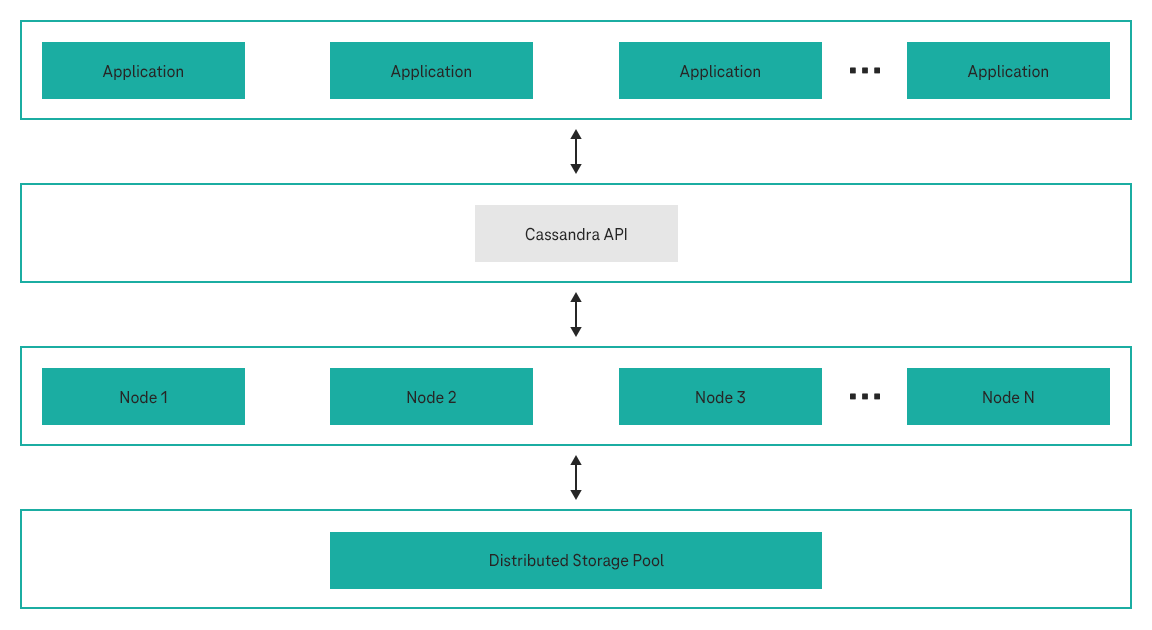
The compute clusters consist of multiple homogeneous nodes, and data is stored in a distributed, shared storage pool. Compute and storage resources are decoupled from each other so they can be flexibly scaled in or out without having to migrate any data.
GeminiDB is a distributed database with decoupled storage and compute architecture. One compute cluster may consist of multiple homogeneous nodes, and data is stored in a distributed, shared storage pool. It allows you to scale compute and storage resources flexibly without having to migrate any data.

Backups are stored in Object Storage Service (OBS) buckets, which provides disaster recovery capabilities and save space. When you create a DB instance, the automated backup policy is enabled by default. After the creation is complete, an automated full backup is triggered instantly. The backup retention period is 7 days by default. You can set the backup retention period and modify the backup policy. In addition, you can initiate backup at any time according to your service requirements. Manual backups are saved until you manually delete them.
GeminiDB uses Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and network security groups to keep DB instances isolated. VPCs allow you to define which IP addresses are allowed to access a given database. Running a DB instance in a VPC improves security. To further enhance database security, you can configure subnets and security groups to control access to DB instances.

VPC security groups can be configured with rules to control traffic to and from DB instances.

GeminiDB supports multi-layer network protection. The security system consists of VPCs, subnets, security groups, Anti-DDoS, and SSL, which collectively can defend against a wide range of attacks and keep your data secure.
- VPCs isolate resources and control access.
- SSL connections ensure data security and integrity.
- Security group rules control traffic to and from specific IP addresses and ports, protecting connections between GeminiDB and other services.
GeminiDB monitors instance performance, reducing 60% of O&M activities. It provides real-time monitoring information about CPU utilization, disk usage, IOPS, and number of active connections, allowing you to check instance status at any time.
Flavor | vCPUs | Memory (GB) | Max. storage space (GB) |
geminidb.cassandra.xlarge.8 | 4 | 32 | 96,000 |
geminidb.cassandra.2xlarge.8 | 8 | 64 | 96,000 |
geminidb.cassandra.4xlarge.8 | 16 | 128 | 96,000 |
geminidb.cassandra.8xlarge.8 | 32 | 256 | 192,000 |
geminidb.cassandra.15xlarge.8 | 60 | 480 | 360,000 |
Compatible API | Instance type | Version |
Cassandra | Cluster | 3.11 & 4.0 |
Elastic Cloud Server (ECS) provides GeminiDB with elastic computing resources. GeminiDB needs to apply for resources from ECS to build a running environment for DB instances.
Backups are stored in Object Storage Service (OBS) buckets, which provides disaster recovery capabilities and saves space.
GeminiDB uses Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and network security groups to keep DB instances isolated. VPCs allow you to define which IP addresses are allowed to access a given database. Running a DB instance in a VPC improves security.
Cloud Eye serves as an open monitoring platform, keeping track of GeminiDB resources for you. It reports alarms and promptly issues warnings to ensure that services remain running properly.
GeminiDB provides excellent read and write performance, flexibility, and fault tolerance, making it easy for those websites that provide product catalogs, recommendations, personalization engines, and transaction records to handle high concurrency and ensure low latency.
Advantages
- Large-scale clusters: Each cluster can include up to 200 nodes, helping write-intensive Internet applications process massive volumes of data.
- High availability and scalability: The failure of one node does not affect the availability of the entire cluster. Compute resources and storage space can be quickly scaled up with minimal service interruptions.
- High availability and scalability: The failure of one node does not affect the availability of the entire cluster. Compute resources and storage space can be quickly scaled up with minimal service interruptions.
GeminiDB is fully compatible with Cassandra, so it can help you collect, organize, and store data from different types of terminals, as well as aggregate and analyze the data in real-time.
Advantages
- Large-scale clusters: The large-scale clusters are well suited to collect and store massive numbers of manufacturing metrics.
- High availability and performance: Data can be written to this database 24/7.
- Fast backup and restoration: Snapshots allow for fast backup and recovery.
- Scaling in minutes: Service or project peaks can be handled easily.
Performance ratio of GeminiDB to open-source Cassandra (ECS with Data disk type: Ultra-high I/O)
Engine | Selected Hardware (flavors) | Concurrent client threads | Data used | 95% read and 5% update | 50% read and 50% update | 65% read, 25% update and 10% insert | 90% insert and 10% read |
Open-Source Cassandra Cluster | 4 vCPUs 6 GB | 32 | 50 GB | 2884 | 5068 | 8484 | 10694 |
Open-Source Cassandra Cluster | 8 vCPUs 32 GB | 64 | 100 GB | 2796 | 2904 | 5180 | 7854 |
Open-Source Cassandra Cluster | 16 vCPUs 64 GB | 128 | 200 GB | 5896 | 14776 | 14304 | 15707 |
Open-Source Cassandra Cluster | 32 vCPUs 128 GB | 256 | 400 GB | 8964 | 22284 | 19592 | 22344 |
GeminiDB | 4 vCPUs 6 GB | 32 | 50 GB | 8439 | 10565 | 9468 | 23830 |
GeminiDB | 8 vCPUs 32 GB | 64 | 100 GB | 24090 | 24970 | 21716 | 44548 |
GeminiDB | 16 vCPUs 64 GB | 128 | 200 GB | 48985 | 51335 | 43557 | 67290 |
GeminiDB | 32 vCPUs 128 GB | 256 | 400 GB | 91280 | 85748 | 74313 | 111540 |
The GeminiDB performs ten times better than the open-source Cassandra cluster in read latency.
The GeminiDB cluster gives you nearly identical write performance as the open-source cluster.
Adding nodes slightly affects both the GeminiDB and open-source clusters.
- The scale-out process of GeminiDB is fast and affects services for a short period of time (10s). You do not need to change parameters, and the scale-out process lasts for 10 minutes.
- For an open-source Cassandra cluster, the duration for adding nodes depends on the data volume and parameter settings, and the impact on performance varies. In a test scenario, the scaling took more than 30 minutes when the preset data size is 50 GB.
- In a multiple-node instance with 4 vCPUs per node there should be no more than 250 GB on each node, and the transactions per second (TPS) on each node are limited to 1000.
- In a multiple-node instance with 8 vCPUs per node there should be no more than 250 GB on each node, and the transactions per second (TPS) on each node are limited to 2500.
- In a multiple-node instance with 16 vCPUs per node there should be no more than 500 GB on each node, and the transactions per second (TPS) on each node are limited to 5000.
- In a multiple-node instance with 32 vCPUs per node there should be no more than 500 GB on each node, and the transactions per second (TPS) on each node are limited to 10000.
Do not store large data such as images and files in these databases.
The maximum size of the key and value in a single row cannot exceed 64 KB, and the average size of rows cannot exceed 10 KB.
The data deletion policy must be considered in the design of a table. Data in a table cannot increase infinitely without being deleted.
Partition keys can evenly distribute workloads to avoid data skew.
A partition key of a primary key determines a logical partition for storing table data. If partition keys are not evenly distributed, data and load between nodes are unbalanced, resulting in a data skew problem.
The design of partition keys can evenly distribute data access requests to avoid BigKey or HotKey issues.
- BigKey issue: The main cause of BigKey is that the primary key is improperly designed. As a result, there are too many records or too much data in a single partition. Once a partition becomes extremely large, access to the partition increases the load of a server where the partition is located and can even cause an Out of Memory (OOM) error.
- HotKey issue: This issue occurs when a key is frequently operated in a short period of time. For example, breaking news can cause a spike in traffic and large number of requests. As a result, the CPU usage and the load on the node on which the key is located increase, affecting other requests to the node and reducing the success rate of services. HotKey issues will also occur, e.g., during the promotion of popular products and Internet celebrity live streaming.
The number of rows of a single partition key cannot exceed 100,000, and the disk space of a single partition cannot exceed 100 MB.
The size of records under a single partition key cannot exceed 100 MB.
Ensure strong consistency between data copies written to GeminiDB, but do not support transactions.
Consistency model | Consistency supported | Description |
Concurrent write consistency | Yes | GeminiDB does not support transactions, and data writing is strongly consistent. |
Consistency between tables | Yes | GeminiDB does not support transactions, and data writing is strongly consistent. |
Data migration consistency | Eventual consistency | DRS migration provides data sampling, comparison, and verification capabilities. After services are migrated, data verification occurs automatically. |
For large-scale storage, database splitting must be considered. Ensure that the number of nodes in the GeminiDB cluster is less than 100. If the number of nodes exceeds 100, split the cluster vertically or horizontally.
Vertical splitting: Data is split by functional module, for example, the order database, product database, and user database. In this mode, the table structures of multiple databases are different.
Horizontal sharding: Data in the same table is divided into blocks and stored in different databases. The table structures in these databases are the same.
Avoid tombstones caused by large-scale deletion.
- Use TTL instead of Delete if possible.
- Do not delete a large amount of data. Delete data by primary key prefix.
- A maximum of 1,000 rows can be deleted at a time within a partition key.
- Avoid querying deleted data during range query.
- Do not frequently delete data of a large range in one partition.
Properly control the database scale and quantity. It is recommended that the number of data records in a single table be less than or equal to 100 billion. It is also recommended that a single database contains no more than 100 tables and that the maximum number of fields in a single table be 20 to 50.
Estimate how many resources GeminiDB servers can process. If it is estimated that N nodes need to be used, adding additional N/2 nodes is recommended for fault tolerance and performance consistency. In normal scenarios, the CPU usage of each node is limited to 50% to avoid fluctuation during peak hours.
To store large volumes of data, perform a test run based on service scenarios. In service scenarios with a large number of requests and data volume, you need to test the performance in advance because the service read/write ratio, random access mode, and instance specifications vary greatly.
Split database cluster granularity properly.
- In distributed scenarios, microservices of a service can share a GeminiDB cluster to reduce resource and maintenance costs.
- The service can be divided into different clusters based on the data importance, number of tables, and number of records in a single table.
Do not frequently update fields in a single data record.
If there are too many nested elements such as List, Map, or Set, read and write performance will be affected. In this case, convert such elements into JSON data for storage.
Neue Features
Learn more


